Web 3.0, known as the Semantic Web, is an evolution of the internet that aims to make data more interconnected and intelligent. It holds promise for more personalized and efficient online experiences, enabling machines to better understand and interpret data to provide a Smooth and continuous and attractive user experience.
Evaluation among web1.0, web2.0, and web 3.0
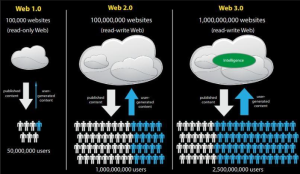
Web 1.0 refers to the early days of the internet where the web was primarily used for sharing information in a static, one-way manner. Websites were basic, with limited interactivity, and users were only able to consume content.
Web 2.0 introduced a more interactive and social web, with the rise of social media platforms and user-generated content. Users were able to create, share, and interact with content, leading to a more collaborative and participatory web.
Web 3.0, also known as the Semantic Web, is a future vision of the internet where data is more interconnected and intelligent. This would allow machines to better understand and interpret data, leading to more personalized and efficient online experiences.
Overall, each phase of the web has brought new innovations and changes to how we interact with the internet, and the development of the Semantic Web holds great promise for the future.
Need of Web 3.0 Nowadays
The need for Web 3.0 arises from the limitations of the current web. With Web 2.0, there is an over-reliance on centralized services, which can lead to issues such as data breaches and censorship. Web 3.0 aims to address these issues by providing a more decentralized and secure internet, where users have greater control over their data and interactions. Additionally, the Semantic Web holds promise for more efficient and personalized online experiences. Overall, Web 3.0 is necessary to improve the internet’s functionality, security, and user experience in the face of growing concerns around privacy and control of data.
Advantages of Web 3.0:
Decentralization:
Web 3.0 aims to provide a more decentralized internet, where users have greater control over their data and interactions.
Security:
With Web 3.0, users can enjoy enhanced security due to the use of advanced cryptographic techniques and decentralized systems.
Efficiency:
The Semantic Web holds promise for more efficient and personalized online experiences, as machines can better understand and interpret data.
Interoperability:
Web 3.0 allows for greater interoperability between different applications, platforms, and devices.
Disadvantages of Web 3.0:
Technical complexity:
The development of Web 3.0 requires complex technical infrastructure, which can be difficult and expensive to implement.
Learning curve:
With the introduction of new concepts and technologies, users may need to learn new skills to take advantage of Web 3.0.
Adoption:
The success of Web 3.0 depends on widespread adoption, which may take time to achieve.
Governance:
Decentralization can also pose challenges for governance, as it can be difficult to ensure accountability and address disputes in a decentralized system.
Web 3.0 use cases and applications
Web 3.0 has a wide range of potential use cases and applications, including decentralized finance (DeFi), digital identity management, supply chain management, content monetization, and more. It also enables the development of decentralized applications (dApps) and non-fungible tokens (NFTs), with potential applications in gaming, art, and collectibles.
The potential benefits of Web 3.0
Web 3.0 has the potential to provide a more decentralized and secure internet, where users have greater control over their data and interactions. It can also lead to more efficient and personalized online experiences through the use of the Semantic Web. Additionally, Web 3.0 allows for greater interoperability between different applications, platforms, and devices, and can enable new forms of decentralized applications and transactions.





