The 1970s saw a surge of interest in electric vehicle technology, coinciding with the rise in gas prices. This led the US Congress to pass the Electric and Hybrid Vehicle Research, Development, and Demonstration Act in 1976. By the 1990s, concerns about transportation emissions prompted manufacturers to modify models for electric charging, and GM’s EV1 electric vehicle was developed.
Impact of Electric Vehicles on the Environment and Society
The emergence of electric vehicles can bring significant benefits, such as reducing greenhouse gas emissions and improving air quality, which would greatly benefit the environment and public health. Moreover, the development of electric vehicles has the potential to generate new employment opportunities in the manufacturing, charging station installation, and battery recycling industries.
Nonetheless, the widespread adoption of electric vehicles may also have some adverse effects on the environment and society. One of these is the potential increase in greenhouse gas emissions from power plants, mainly if they utilize fossil fuels to generate electricity to power the vehicles. Additionally, producing electric cars requires natural resources such as rare earth metals, which can be environmentally damaging to extract from the earth.
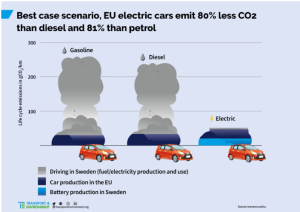
The future of electric vehicles
However, the future of electric vehicles looks promising globally. Many countries and automakers have set ambitious goals for phasing out traditional gasoline-powered vehicles and transitioning to electric vehicles. The International Energy Agency has projected that there will be 145 million electric vehicles on the road by 2030, and this number could grow to over 230 million by 2035. Electric vehicle technology is also advancing rapidly, with battery and charging infrastructure improvements, making electric vehicles increasingly practical and affordable for more people. Moreover, the push towards electric vehicles is driven by concerns over climate change and air pollution, leading to stricter emissions regulations and incentives for electric vehicle adoption. Overall, the future of electric vehicles is one of growth and transformation in the global transportation sector.
Why are Electric Vehicles a Boon?
EVs have many global benefits, including the reduction of greenhouse gas emissions. The global stock of electric passenger cars reached 10 million in 2020, avoiding the release of 40 million tons of CO2 emissions. EVs also emit zero pollutants at the tailpipe, improving air quality in cities and reducing health costs. They have lower operating and maintenance costs than traditional vehicles, with the total cost of ownership of EVs expected to be lower than that of conventional cars in most markets by 2030. The growth of the EV industry has created new job opportunities, particularly in manufacturing and battery production, which could lead to the creation of 10 million new jobs worldwide by 2030. EVs also reduce dependence on imported oil, improving energy security for countries. Overall, the global benefits of EVs are significant, with the adoption of EVs expected to continue to increase.
Don’t Be Shocked
Electric vehicles (EVs) are gaining ground.
- Volkswagen pledged to halt sales of internal combustion engine (ICE) vehicles in Europe by 2035.
- Ford has said it will only sell EVs in Europe by 2030.
- Volvo said it is retiring the ICE engine and hybrids by 2030.
- Honda announced plans to phase out gas-powered cars by 2040.
- General Motors has said it will stop building polluting vehicles by 2035.





