What is Blockchain?
Blockchain is a type of shared, immutable ledger that facilitates the process of recording transactions and tracking assets in a business network. An asset can be tangible (house, car, cash, land) or intangible (intellectual property, patents, copyrights, branding).
Blockchain comprises of a database that differs from a typical database in the way that it stores information; blockchains store data in blocks that are then linked together via cryptography. As new data comes in, it is entered into a fresh block. Once the block is filled with data, it is chained onto the previous block, which connects the data in chronological order.
Virtually anything of value can be tracked and traded on a blockchain network, reducing risk and cutting costs for all involved.
How does Blockchain Work?
The goal of blockchain is to allow digital information to be recorded and distributed, but not edited. In this way, a blockchain is the foundation for immutable ledgers, or records of transactions that cannot be altered, deleted, or destroyed. This is why blockchains are also known as distributed ledger technology (DLT).
Transaction Process
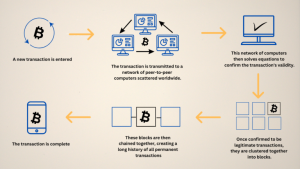
Pros and Cons of Blockchain
For all its complexity, blockchain’s potential as a decentralized form of record-keeping is almost without limit. From greater user privacy and heightened security to lower processing fees and fewer errors, blockchain technology may very well see applications beyond those outlined above. But there are also some disadvantages.
Pros
- Improved accuracy by removing human involvement in verification.
- Cost reductions by eliminating third-party verification.
- Decentralization makes it harder to tamper with.
- Transactions are secure, private, and efficient.
- Transparent technology.
- Provides a banking alternative and a way to secure personal information for citizens of countries with unstable or underdeveloped governments.
Cons
- Significant technology cost associated with mining bitcoin.
- Low transactions per second.
- History of use in illicit activities, such as on the dark web.
- Regulation varies by jurisdiction and remains uncertain.
- Data storage limitations.
Benefits of using Blockchain Technology
1. Decentralization
Blockchain being a decentralized system, one cannot create an authority and manipulate the system according to their own needs. It uses a peer-to-peer network, and the system is shared among everyone. This decentralized system is a revolutionary idea which has the potential to replace traditional centralized systems, where few people have the authority to make decisions.
2. Immutability
With Blockchain, there is no possibility of changing the data or altering the data. The data present inside the Blockchain is permanent and no one can delete or undo it.
3. Transparency
By utilizing Blockchain technology, organizations and enterprises can go for a completely decentralized network where there is no need for any centralized authority, thus improving the transparency of the entire system.
4. High Availability
In the Blockchain network, everyone is on a P2P network, and everyone has a computer running, therefore, even if one peer goes down, the other peers still work.
5. High Security
Technology is assumed to offer high security as all the transactions of Blockchain are cryptographically secure and provide integrity. Thus, instead of relying on third-party, you need to put your trust in cryptographic algorithms.
6. Efficiency
Blockchain technology has the potential to streamline processes and reduce the need for intermediaries, which can increase efficiency and reduce costs to a great extent.
Future of Blockchain
The scope of blockchain technology will expand in the coming years, and the merits of its application will lure businesses and organizations globally to invest in it. Although blockchain technology is in its nascent stage, its future is poised to see adoption from industries across the globe.





